Meeting the Minimum Security Criteria (MSC) for the CTPAT Risk Assessment
Whether you’re new to CTPAT certification or are preparing for validation or recertification, the U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s (CBP)...
Of all the major program changes we’ve seen in the last year, new CTPAT Agricultural Security requirements continue to throw supply chain professionals for a loop. So what exactly are the rules, and how do you go about following them? In this article, we answer your top eight most frequently asked questions about Agricultural Security for CTPAT to help your organization stay fully compliant with CBP protocol.
Every year, there are billions of pounds of products entering the U.S., including millions of pounds of agricultural products. To prevent the introduction of harmful plants, pests, animal diseases, and invasive species, a new agricultural inspection component has been added to the CTPAT container loading process. The agricultural inspection standards are necessary to ensure structures don’t harbor organic contraband or haven’t been contaminated with agricultural pests.
U.S. Customs officially defines pest contamination as “visible forms of animals, insects, or other invertebrates (alive or dead, in any lifecycle stage, including egg casings or rafts), or any organic material of animal origin (including blood, bones, hair, flesh, secretions, excretions); viable or non-viable plants or plant products (including fruit, seeds, leaves, twigs, roots, bark); or other organic material, including fungi; or soil, or water.”
So there you have it! (And, for those of you feeling a little sick to your stomachs after reading that explanation, you’re not alone…it makes us a bit queasy too)
Pest inspections are mandatory for all forms of international travel and transport. This includes ocean containers, refrigerated containers and trailers, over-the-road trailers, flatbed trailers, tank containers, rail and boxcars, hoppers, and unit load devices (ULDs). Overseas supply chain expectations are that this inspection takes place at the point of cargo packing.
If you stuff or load containers, your team is required to execute agricultural inspections for every container. Here is a summary of what you need to do to meet the Minimum Security Requirement for Container Load:
The 7-Point / 8-Point and 17-Point / 18-Point Inspections have very specific requirements. The most important of which is if you see any evidence of infestation in the container or the agriculture itself during an inspection (i.e. bugs, animals, mold, or any other potential environmental contaminants), you must halt the loading or movement of the container and alert your supervisor, along with the proper authorities.
After you sound the metaphorical pest alarm, there is a chance you may be able to salvage at least a portion of the cargo by sanitizing the container and transferring any unaffected cargo to another one. If you do run into a serious contamination issue, remember you can always get CBP involved by calling 1-800-BE-ALERT.
There are also new CTPAT agricultural security requirements for WPM (Wood Packing Material. Under MSC guidelines, only ISPM15 (International Standard for Phytosanitary Measures) approved WPM is permitted in containers traveling across the border. This means that all wooden shipping materials must also meet the requirements, including (but not limited to): crates, pallets, boxes, and any other wood being used to support or brace cargo.
To put this rule simply, if you’re traveling with wood in a container, every piece must meet ISPM 15 standards. Period.
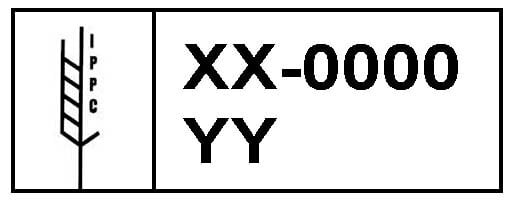
To figure out if the wood in your container is compliant with CBP protocol, check for a stamp (either ink or burned/branded) that looks like the image below:
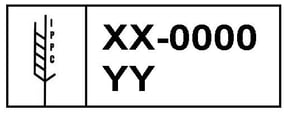
There can be some variation in the ISPM15 seal, but many elements must be exactly as shown. Here’s a quick breakdown to help tell if the stamp is legitimate, using the example above as a reference:
IMPORTANT NOTE: Firewood should never be transported unless you have a special license permitting you to do so. If you do have a license, remember that the only type of firewood approved for transport across state lines is specially heated to kill pests and sealed with a governmental stamp.
Because this new agricultural policy is such a critical issue, Customs and Border Protection doesn’t solely rely on CTPAT Members to manage all the elements. CBP also helps by conducting random inspections at the port of entry for agricultural cargo. Currently, these searches are conducted in the form of a visual spot-check that includes looking for dirt, bugs, organic material, and soil. However, the future inspection technique will involve canine units and specialized X-ray machines designed to detect organic material.
Ultimately, the goal of these requirements is to get CTPAT members and CBP working together to help better protect U.S. farmlands, forests, and lakes – all of which have a direct impact on the economy, environment, and health of United States residents. (Thanks for doing your part!)
We hope this information helps you better understand and comply with new CTPAT Agricultural Security regulations. However, if you find yourself in need of a more detailed understanding of this or any other CTPAT requirement, Veroot has you covered.
Whether you’re new to CTPAT certification or are preparing for validation or recertification, the U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s (CBP)...

Have you ever wondered how much trust really matters in global trade? A lot more than you think. When your business relies on partners around the...

The world of Global Trade does not stand still, and neither does CTPAT.Over the years, the CTPAT Minimum Security Criteria (MSC) have evolved to...